Researchers are using deep learning to create a new laser-based system that can peer around corners in real-time. This may allow self-driving cars to look around parked cars or busy intersections for hazards or pedestrians.
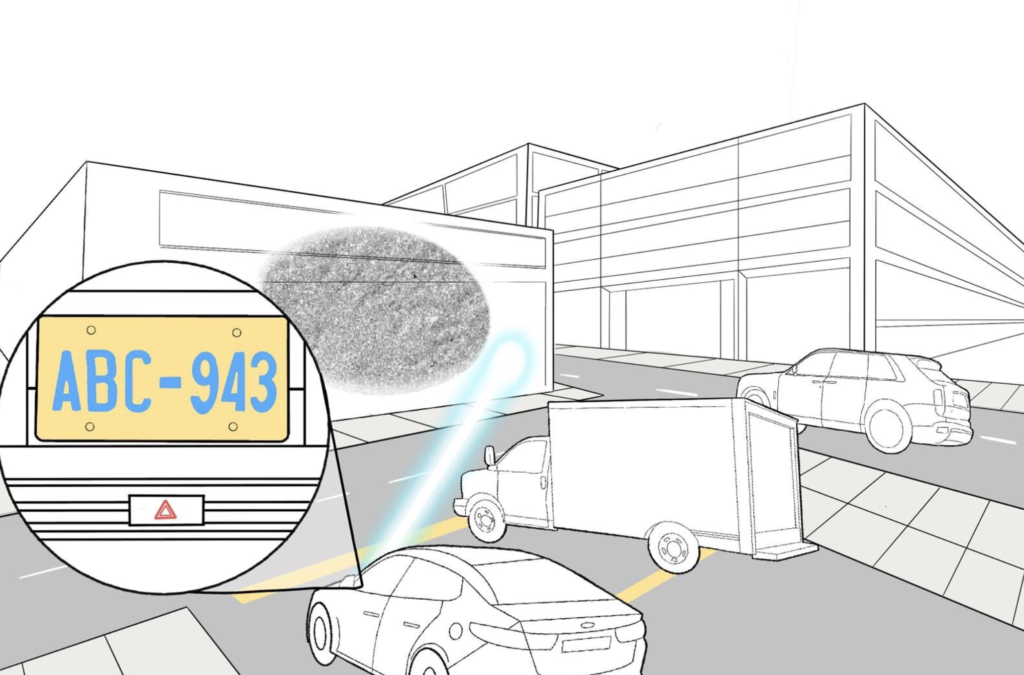
“Compared to other approaches, our non-line-of-sight imaging system provides uniquely high resolutions and imaging speeds,” said research team leader Christopher A. Metzler from Stanford University and Rice University. “These attributes enable applications that wouldn’t otherwise be possible, such as reading the license plate of a hidden car as it is driving or reading a badge worn by someone walking on the other side of a corner.”
Metzler and colleagues from Princeton University, Southern Methodist University, and Rice University report that the imaging system can distinguish submillimeter details of a hidden object from one meter away. The system is designed to image small objects at very high resolutions but can be combined with other imaging systems that produce low-resolution room-sized reconstructions.
“Non-line-of-sight imaging has important applications in medical imaging, navigation, robotics and defense,” said co-author Felix Heide from Princeton University. “Our work takes a step toward enabling its use in a variety of such applications.”
How does it work?
The imaging system uses a camera sensor and laser source similar to the one found in a laser pointer and bounces the laser beam bounces off a visible wall onto the hidden object and then back onto the wall, creating an interference pattern known as a speckle pattern that encodes the shape of the hidden object.
The system then reconstructs the hidden object from the speckle pattern requires solving a challenging computational problem. Short exposure times are necessary for real-time imaging but produce too much noise for existing algorithms to work. To solve this problem, the researchers turned to deep learning.
“Compared to other approaches for non-line-of-sight imaging, our deep learning algorithm is far more robust to noise and thus can operate with much shorter exposure times,” said co-author Prasanna Rangarajan from Southern Methodist University. “By accurately characterizing the noise, we were able to synthesize data to train the algorithm to solve the reconstruction problem using deep learning without having to capture costly experimental training data.”
The research is part of DARPA’s Revolutionary Enhancement of Visibility by Exploiting Active Light-fields (REVEAL) program, which is developing a variety of different techniques to image hidden objects around corners. The researchers are now working to make the system practical for more applications by extending the field of view so that it can reconstruct larger objects.